Gene editing
What is a gene?
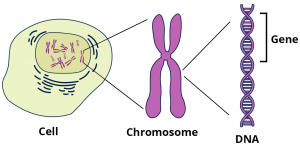
Gene is part of a long DNA molecule that is packed inside each cell of all living organisms starting from simple single-cell microorganisms to complex multicellular organisms.
DNA is an instruction manual in an organism, it is responsible for various traits we see such as the colour of our eyes. DNA is inherited from the parents. Each organism has two sets of genes for a character, one from each parent. These new sets of genes produce new instructions which get reshuffled in each generation. However, sometimes these genes may contain faulty instructions which may lead to serious illnesses.
Can the error in genes be corrected?
In a document, if we have misspelled a word, we use the ‘find’ function to
highlight the error and correct it or delete it.
Imagine using ‘find and
replace’ technique to find a faulty gene in a DNA sequence. This is possible
using gene editing.
How does gene editing work?
Gene editing is a group of techniques which enable scientists to manipulate the organism’s DNA. This technique enables genetic material to be added, removed, or altered at a particular location in the genome.
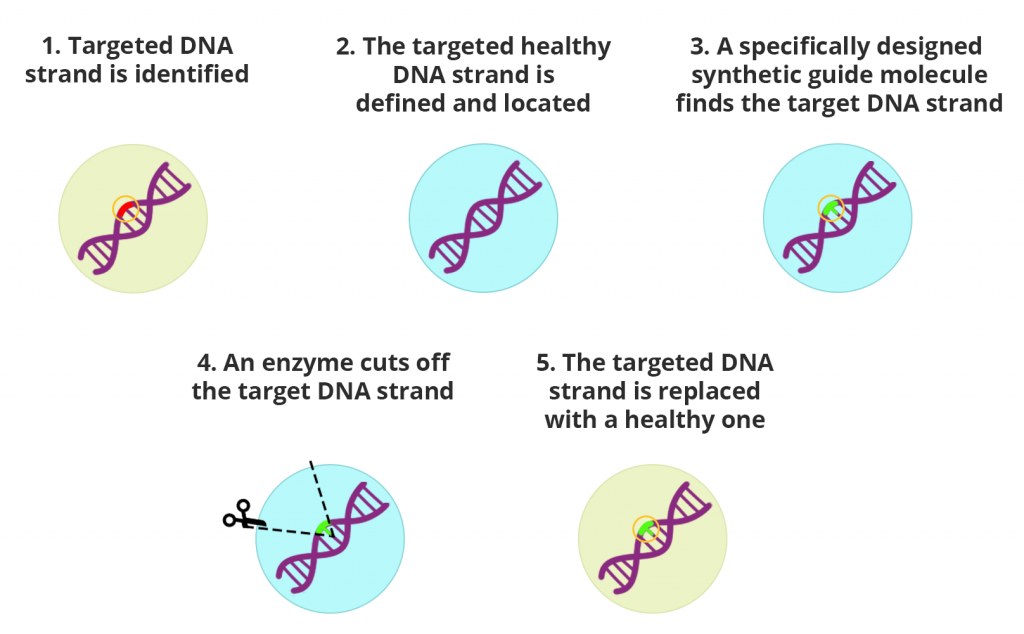
Scientists have figured out many ways to modify genes. E.g. crossbreeding of plants to produce a better yield. But the use of gene editing to modify genes has proved to be one of the best techniques.
The technique of gene editing promises huge benefits as it is faster, simpler,
and cheaper as compared to older methods of gene modification.
One of the recent gene editing techniques is done by using CRISPR-Cas9.
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats is a sequence information present in a bacterial genome, which is regularly interspaced and repetitive in nature. CRISPR is associated with a protein called Cas9 which acts as a molecular scissor.
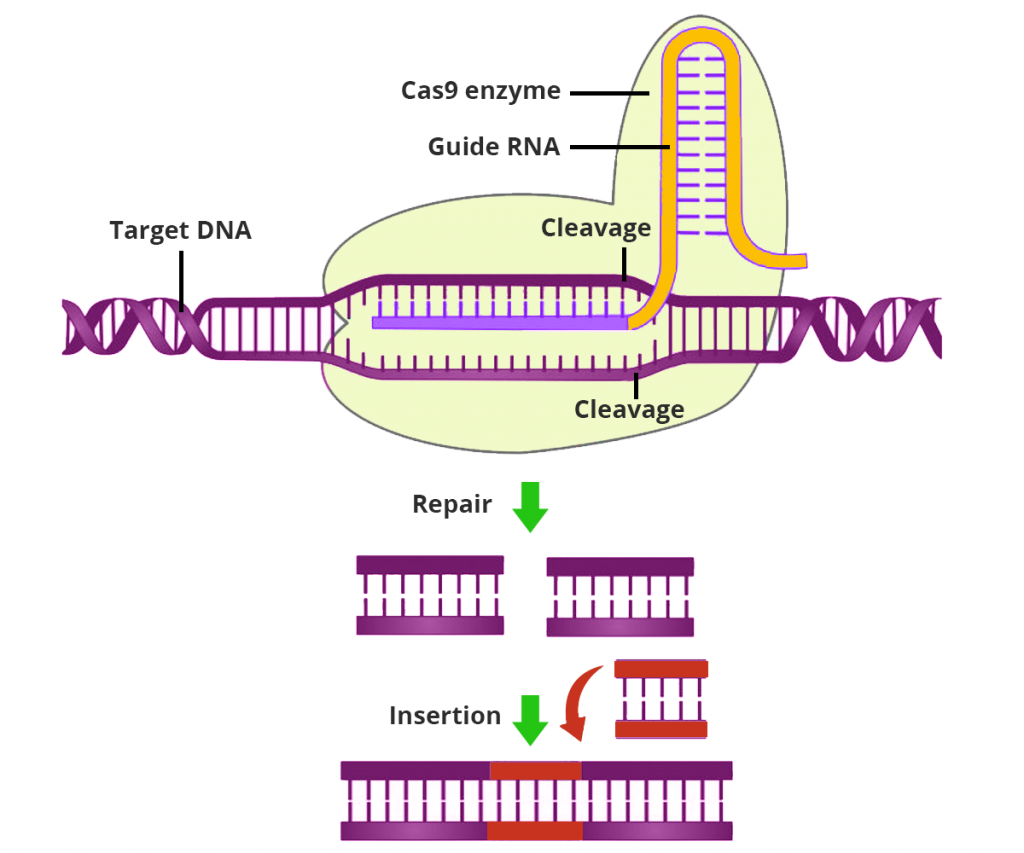
CRISPR (guide RNA) is used to pinpoint the precise DNA sequence in a gene to be altered and the enzyme Cas9 snips through the DNA by changing it or allowing it to be replaced by a new DNA sequence.
Gene editing has the potential to modify the DNA of an organism. It can be used to fix the gene mutation that can cause cancer. It enables scientists to come up with new therapy for viral diseases, to edit genes that cause hereditary diseases, make crops more nutritious and disease resistant, etc.
Even though gene editing has many potential benefits, it has some serious negative implications too. E.g. editing human embryos or to manipulate and design features of a baby, developing more virulent microbial diseases, etc.
The negative implications pose many ethical and social concerns. Gene editing has the potential to provide life-changing solutions to some of the world’s biggest challenges. Thus, we need to find a way to regulate its usage in order to avoid the negative implication and help flourish the positive ones.
– Suchasmita Panigrahi
